Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Sample and Feature Selection with FPS and CUR¶
- Authors:
Davide Tisi @DavideTisi and Hanna Tuerk @HannaTuerk
In this tutorial we generate descriptors using featomic, then select a subset of structures using both the farthest-point sampling (FPS) and CUR algorithms implemented in scikit-matter. Finally, we also generate a selection of the most important features using the same techniques.
First, import all the necessary packages
import os
import ase.io
import chemiscope
import metatensor
import numpy as np
import requests
from featomic import SoapPowerSpectrum
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from skmatter import feature_selection, sample_selection
from urllib3.util.retry import Retry
Load structure data¶
Load 500 example Ga/As structures from file, reading them using ASE.
def fetch_dataset(filename, base_url, local_path=""):
"""Helper function to load data with retries on errors."""
local_file = local_path + filename
if os.path.isfile(local_file):
return
# Retry strategy: wait 1s, 2s, 4s, 8s, 16s on 429/5xx errors
retry_strategy = Retry(
total=5, backoff_factor=1, status_forcelist=[429, 500, 502, 503, 504]
)
session = requests.Session()
session.mount("https://", requests.adapters.HTTPAdapter(max_retries=retry_strategy))
# Fetch with automatic retry and error raising
response = session.get(base_url + filename)
response.raise_for_status()
with open(local_file, "wb") as file:
file.write(response.content)
filename = "gaas_training.xyz"
fetch_dataset(filename, "https://zenodo.org/records/10566825/files/")
# Load a subset of structures from the example dataset
n_frames = 500
frames = ase.io.read("gaas_training.xyz", f":{3 * n_frames}:3", format="extxyz")
Compute SOAP descriptors using featomic¶
First, define the featomic hyperparameters used to compute SOAP features.
# featomic hyperparameters
hypers = {
"cutoff": {"radius": 6.0, "smoothing": {"type": "ShiftedCosine", "width": 0.5}},
"density": {
"type": "Gaussian",
"width": 0.3,
"scaling": {"type": "Willatt2018", "exponent": 4, "rate": 1, "scale": 3.5},
},
"basis": {
"type": "TensorProduct",
"max_angular": 6,
"radial": {"type": "Gto", "max_radial": 7},
},
}
# Generate a SOAP power spectrum
calculator = SoapPowerSpectrum(**hypers)
rho2i = calculator.compute(frames)
# Makes a dense block
atom_soap = rho2i.keys_to_properties(["neighbor_1_type", "neighbor_2_type"])
atom_soap_single_block = atom_soap.keys_to_samples(keys_to_move=["center_type"])
# Sum over atomic centers to compute structure features
struct_soap = metatensor.sum_over_samples(
atom_soap_single_block, sample_names=["atom", "center_type"]
)
print("atom feature descriptor shape:", atom_soap.block(0).values.shape)
print(
"atom feature descriptor (all in one block) shape:",
atom_soap_single_block.block(0).values.shape,
)
print("structure feature descriptor shape:", struct_soap.block(0).values.shape)
atom feature descriptor shape: (93670, 1344)
atom feature descriptor (all in one block) shape: (148821, 1344)
structure feature descriptor shape: (500, 1344)
Perform atomic environment (i.e. sample) selection¶
Using FPS and CUR algorithms, we can perform selection of atomic environments. These are implemented in skmatter which uses data stored in the metatensor format.
Suppose we want to select the 10 most diverse environments for each chemical species.
First, we can use the keys_to_properties operation in metatensor to move the neighbor species indices to the properties of the TensorBlocks. The resulting descriptor will be a TensorMap comprised of three blocks, one for each chemical species, where the chemical species indices are solely present in the keys.
print("----Atomic environment selection-----")
print(atom_soap)
print(atom_soap.block(0))
----Atomic environment selection-----
TensorMap with 2 blocks
keys: center_type
31
33
TensorBlock
samples (93670): ['system', 'atom']
components (): []
properties (1344): ['neighbor_1_type', 'neighbor_2_type', 'l', 'n_1', 'n_2']
gradients: None
select 10 atomic environments for each chemical species.
# Define the number of structures *per block* to select using FPS
n_envs = 10
# FPS sample selection
for key, block in atom_soap.items():
sample_fps = sample_selection.FPS(n_to_select=n_envs, initialize="random").fit(
atom_soap.block(key).values
)
sample_fps_idxs = sample_fps.selected_idx_
# Print the selected envs for this block
print("atomic envs selected with FPS:\n")
selected_structures_idx = atom_soap.block(key).samples.values[sample_fps_idxs]
newblock = metatensor.slice_block(block, axis="samples", selection=sample_fps_idxs)
print("center_type:", key, "\n(struct_idx, atom_idx)\n", newblock.samples.values)
# CUR sample selection
for key, block in atom_soap.items():
sample_cur = sample_selection.CUR(n_to_select=n_envs).fit(
atom_soap.block(key).values
)
print("atomic envs selected with CUR:\n")
newblock = metatensor.slice_block(
block, axis="samples", selection=sample_cur.selected_idx_
)
print("center_type:", key, "\n(struct_idx, atom_idx)\n", newblock.samples.values)
atomic envs selected with FPS:
center_type: LabelsEntry(center_type=31)
(struct_idx, atom_idx)
[[362 45]
[118 103]
[431 169]
[301 84]
[301 116]
[ 24 224]
[370 360]
[314 134]
[389 336]
[423 38]]
atomic envs selected with FPS:
center_type: LabelsEntry(center_type=33)
(struct_idx, atom_idx)
[[ 23 123]
[311 147]
[442 87]
[161 288]
[307 259]
[174 89]
[212 179]
[224 73]
[285 245]
[398 46]]
atomic envs selected with CUR:
center_type: LabelsEntry(center_type=31)
(struct_idx, atom_idx)
[[118 184]
[ 24 156]
[148 276]
[ 75 131]
[362 280]
[295 232]
[308 256]
[235 59]
[246 163]
[236 312]]
atomic envs selected with CUR:
center_type: LabelsEntry(center_type=33)
(struct_idx, atom_idx)
[[ 24 287]
[ 16 288]
[ 83 45]
[ 75 95]
[383 163]
[306 322]
[225 237]
[174 183]
[389 87]
[140 179]]
Selecting from a combined pool of atomic environments¶
One can also select from a combined pool of atomic environments and structures, instead of selecting an equal number of atomic environments for each chemical species. In this case, we can move the ‘center_type’ key to samples such that our descriptor is a TensorMap consisting of a single block. Upon sample selection, the most diverse atomic environments will be selected, regardless of their chemical species.
print("----All atomic environment selection-----")
atom_soap_single_block = atom_soap.keys_to_samples(keys_to_move=["center_type"])
print("keys", atom_soap_single_block.keys)
print("blocks", atom_soap_single_block[0])
print("samples in first and only block", atom_soap_single_block[0].samples)
# Using the original SOAP descriptor, move all keys to properties.
# Define the number of structures to select using FPS
n_envs = 10
# FPS sample selection
sample_fps = sample_selection.FPS(n_to_select=n_envs, initialize="random").fit(
atom_soap_single_block.block(0).values
)
sample_fps_idxs = sample_fps.selected_idx_
selected_structures_idxs = atom_soap_single_block.block(0).samples["system"][
sample_fps_idxs
]
newblock = metatensor.slice_block(
atom_soap_single_block.block(0), axis="samples", selection=sample_fps.selected_idx_
)
print(
"atomic envs selected with FPS: \n (struct_idx, atom_idx, center_type) \n",
newblock.samples.values,
)
----All atomic environment selection-----
keys Labels(
_
0
)
blocks TensorBlock
samples (148821): ['system', 'atom', 'center_type']
components (): []
properties (1344): ['neighbor_1_type', 'neighbor_2_type', 'l', 'n_1', 'n_2']
gradients: None
samples in first and only block Labels(
system atom center_type
0 0 31
0 1 31
...
499 358 31
499 359 33
)
atomic envs selected with FPS:
(struct_idx, atom_idx, center_type)
[[146 49 31]
[161 288 33]
[311 147 33]
[118 64 31]
[431 169 31]
[113 235 33]
[ 0 172 33]
[ 24 224 31]
[301 139 31]
[100 289 33]]
Perform structure (i.e. sample) selection with FPS/CUR¶
Instead of atomic environments, one can also select diverse structures. We can use the sum_over_samples operation in metatensor to define features in the structural basis instead of the atomic basis. This is done by summing over the atomic environments, labeled by the ‘center’ index in the samples of the TensorMap.
Alternatively, one could use the mean_over_samples operation, depending on the specific inhomogeneity of the size of the structures in the training set.
print("----Structure selection-----")
struct_soap = metatensor.sum_over_samples(
atom_soap_single_block, sample_names=["atom", "center_type"]
)
print("keys", struct_soap.keys)
print("blocks", struct_soap[0])
print("samples in first block", struct_soap[0].samples)
# Define the number of structures to select *per block* using FPS
n_structures = 10
# FPS structure selection
sample_fps = sample_selection.FPS(n_to_select=n_structures, initialize="random").fit(
struct_soap.block(0).values
)
struct_fps_idxs = sample_fps.selected_idx_
print("structures selected with FPS:\n", sample_fps.selected_idx_)
# CUR structure selection
sample_cur = sample_selection.CUR(n_to_select=n_structures).fit(
struct_soap.block(0).values
)
struct_cur_idxs = sample_cur.selected_idx_
print("structures selected with CUR:\n", struct_cur_idxs)
# Slice structure descriptor along axis 0 to contain only the selected structures
struct_soap_fps = struct_soap.block(0).values[struct_fps_idxs, :]
struct_soap_cur = struct_soap.block(0).values[struct_cur_idxs, :]
assert struct_soap_fps.shape == struct_soap_cur.shape
print("Structure descriptor shape before selection ", struct_soap.block(0).values.shape)
print("Structure descriptor shape after selection (FPS)", struct_soap_fps.shape)
print("Structure descriptor shape after selection (CUR)", struct_soap_cur.shape)
----Structure selection-----
keys Labels(
_
0
)
blocks TensorBlock
samples (500): ['system']
components (): []
properties (1344): ['neighbor_1_type', 'neighbor_2_type', 'l', 'n_1', 'n_2']
gradients: None
samples in first block Labels(
system
0
1
...
498
499
)
structures selected with FPS:
[172 224 235 160 488 317 375 24 403 472]
structures selected with CUR:
[342 224 267 219 236 235 140 472 68 429]
Structure descriptor shape before selection (500, 1344)
Structure descriptor shape after selection (FPS) (10, 1344)
Structure descriptor shape after selection (CUR) (10, 1344)
Visualize selected structures¶
sklearn can be used to perform PCA dimensionality reduction on the SOAP descriptors. The resulting PC coordinates can be used to visualize the the data alongside their structures in a chemiscope widget.
# Generate a structure PCA
struct_soap_pca = PCA(n_components=4).fit_transform(struct_soap.block(0).values)
assert struct_soap_pca.shape == (n_frames, 4)
Plot the PCA map¶
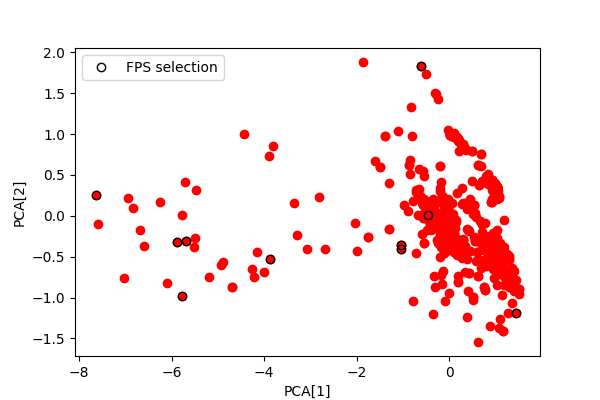
Notice how the selected points avoid the densely-sampled area, and cover the periphery of the dataset
# Matplotlib plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 4))
scatter = ax.scatter(struct_soap_pca[:, 0], struct_soap_pca[:, 1], c="red")
ax.plot(
struct_soap_pca[struct_cur_idxs, 0],
struct_soap_pca[struct_cur_idxs, 1],
"ko",
fillstyle="none",
label="FPS selection",
)
ax.set_xlabel("PCA[1]")
ax.set_ylabel("PCA[2]")
ax.legend()
fig.show()
Creates a chemiscope viewer¶
# Selected level
selection_levels = []
for i in range(len(frames)):
level = 0
if i in struct_cur_idxs:
level += 1
if i in struct_fps_idxs:
level += 2
if level == 0:
level = "Not selected"
elif level == 1:
level = "CUR"
elif level == 2:
level = "FPS"
else:
level = "FPS+CUR"
selection_levels.append(level)
properties = chemiscope.extract_properties(frames)
properties.update(
{
"PC1": struct_soap_pca[:, 0],
"PC2": struct_soap_pca[:, 1],
"PC3": struct_soap_pca[:, 2],
"PC4": struct_soap_pca[:, 3],
"selection": np.array(selection_levels),
}
)
widget = chemiscope.show(
frames,
properties=properties,
settings={
"map": {
"x": {"property": "PC1"},
"y": {"property": "PC2"},
"color": {"property": "energy"},
"symbol": "selection",
"size": {"factor": 50},
},
"structure": [{"unitCell": True}],
},
)
widget.save("sample-selection.json.gz")
# display, if in notebook or sphinx
widget
Perform feature selection¶
Now perform feature selection to reduce the size of the features. In this example we will go back to using the descriptor decomposed into atomic environments, as opposed to the one decomposed into structure environments, but only use FPS for brevity.
print("----Feature selection-----")
print("keys", atom_soap_single_block.keys)
print("blocks", atom_soap_single_block[0])
print("samples in first block", atom_soap_single_block[0].properties)
# Define the number of features to select
n_features = 200
# FPS feature selection
feat_fps = feature_selection.FPS(n_to_select=n_features, initialize="random").fit(
atom_soap_single_block.block(0).values
)
feat_fps_idxs = feat_fps.selected_idx_
atom_soap_single_block_fps = metatensor.slice_block(
atom_soap_single_block.block(0), axis="properties", selection=feat_fps_idxs
)
# Slice atomic descriptor along axis 1 to contain only the selected features
print(
"atomic descriptor shape before selection ",
atom_soap_single_block.block(0).values.shape,
)
print(
"atomic descriptor shape after selection ",
atom_soap_single_block_fps.values.shape,
)
----Feature selection-----
keys Labels(
_
0
)
blocks TensorBlock
samples (148821): ['system', 'atom', 'center_type']
components (): []
properties (1344): ['neighbor_1_type', 'neighbor_2_type', 'l', 'n_1', 'n_2']
gradients: None
samples in first block Labels(
neighbor_1_type neighbor_2_type l n_1 n_2
31 31 0 0 0
31 31 0 0 1
...
33 33 6 7 6
33 33 6 7 7
)
atomic descriptor shape before selection (148821, 1344)
atomic descriptor shape after selection (148821, 200)
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 36.347 seconds)