i-PI¶
i-PI is a universal force engine interface written in Python, designed to be used together with an ab-initio, machine-learned, or force-field based evaluation of the interactions between the atoms. You can see learn more about it on the ipi-code website, the documentation pages or the github repository.
Constant-temperature MD and thermostats
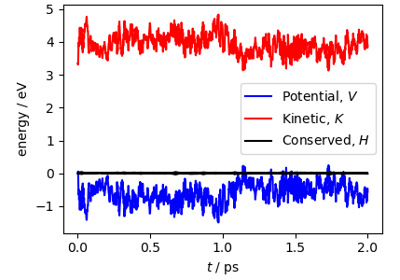
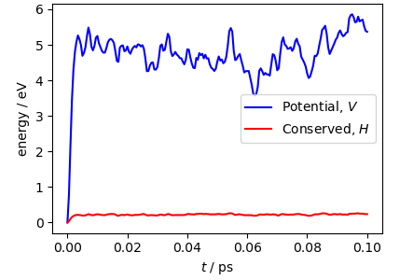
Path integral molecular dynamics
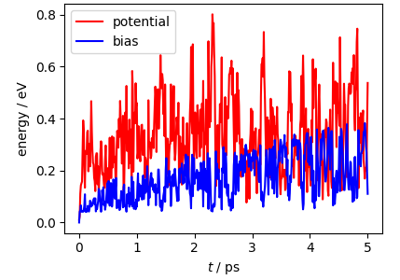
Path integral metadynamics
Quantum heat capacity of water
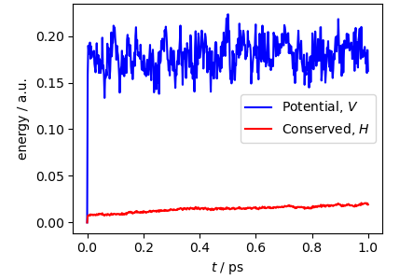
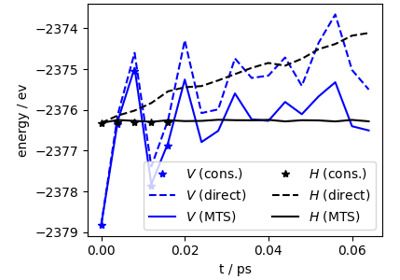
Multiple time stepping and ring-polymer contraction
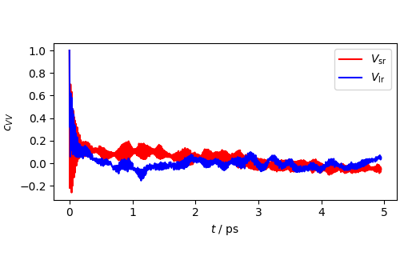
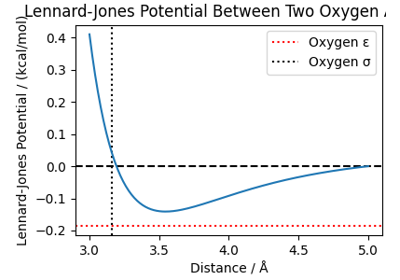
Atomistic Water Model for Molecular Dynamics
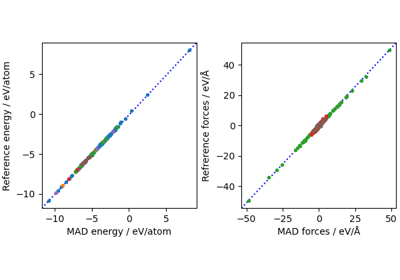
The PET-MAD universal potential
MD using direct-force predictions with PET-MAD
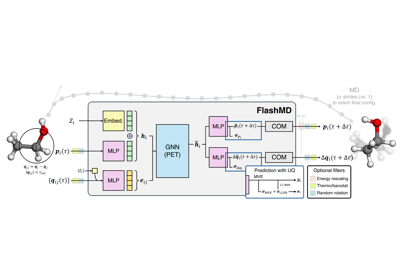
Long-stride trajectories with a universal FlashMD model
ML collective variables in PLUMED with metatomic

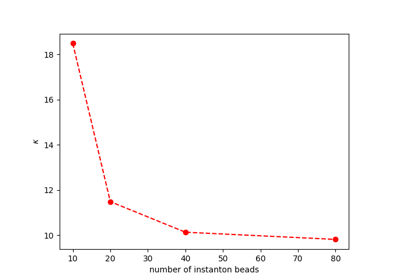
Ring Polymer Instanton Rate Theory: Tunneling Rates