Machine learning models¶
This section contains recipes that concern the training of machine-learning models, or the pre-processing of data to optimize the model architecture or data.
A ML model for the electron density of states

Long-distance Equivariants: a tutorial

Sample and Feature Selection with FPS and CUR

Periodic Hamiltonian learning

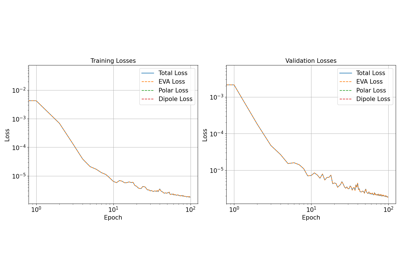
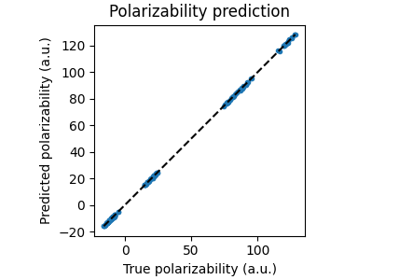
Equivariant linear model for polarizability
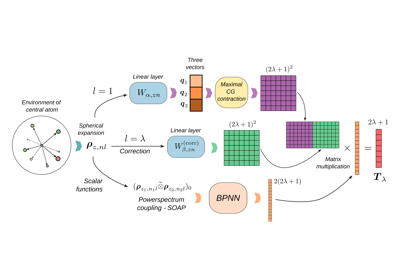
Equivariant model for tensorial properties based on scalar features
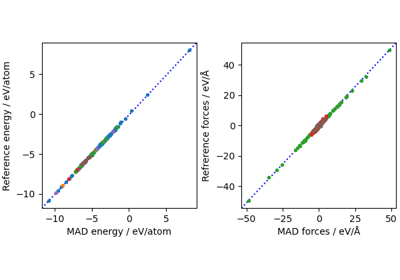
The PET-MAD universal potential
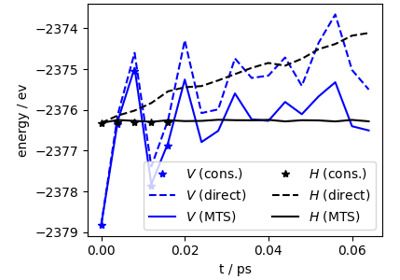
MD using direct-force predictions with PET-MAD
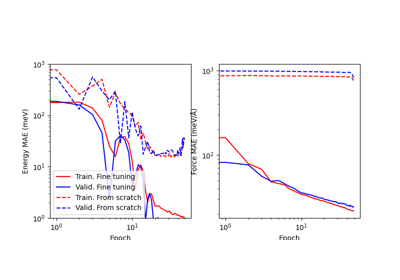
Fine-tuning the PET-MAD universal potential
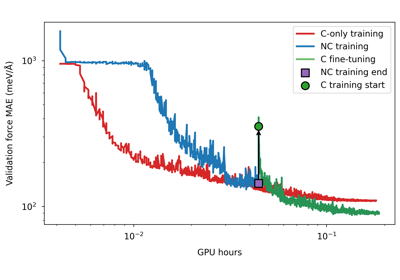
Conservative fine-tuning for a PET model
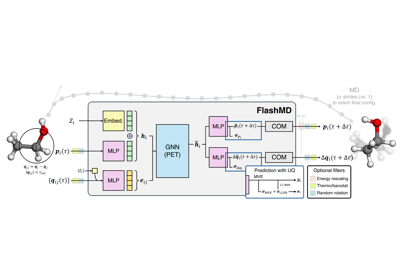
Long-stride trajectories with a universal FlashMD model
Computing NMR shielding tensors using ShiftML
Hamiltonian Learning for Molecules with Indirect Targets